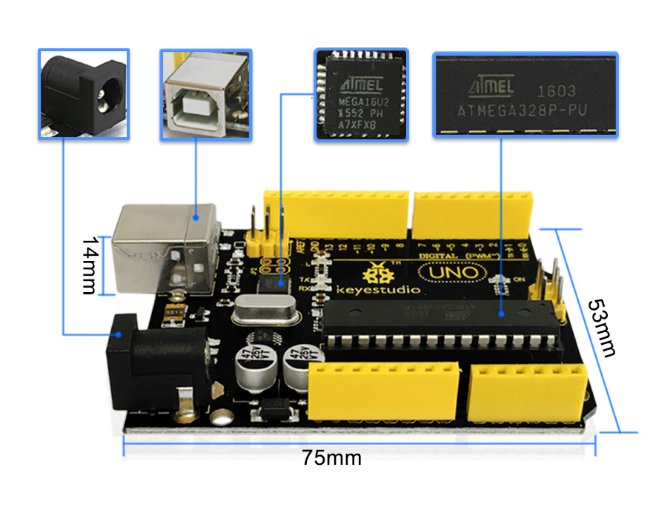
Ks0001 keyestudio UNO R3 BOARD
Introduction
keyestudio Uno R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (datasheet), fully compatible with ARDUINO UNO REV3.
It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, 2 ICSP headers and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to get started.
Note that the two ICSP headers separately used to program the firmware to ATMEGA16U2-MU and ATMEGA328P-PU, but we have programmed the two chips, so generally no need to use them.
The Uno R3 differs from all preceding boards in that it does not use the FTDI USB-to-serial driver chip. Instead, it features the Atmega16U2 programmed as a USB-to-serial converter.
The UNO is the best board to get started with electronics and coding. If this is your first experience tinkering with the platform, the UNO is the most robust board you can start playing with.
Tech Specs
| Microcontroller | ATmega328P-PU |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V |
| Input Voltage (recommended) | 7-12V |
| Digital I/O Pins | 14 (of which 6 provide PWM output) |
| PWM Digital I/O Pins | 6 (D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, D11) |
| Analog Input Pins | 6 (A0-A5) |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 20 mA |
| DC Current for 3.3V Pin | 50 mA |
| Flash Memory | 32 KB (ATmega328) of which 0.5 KB used by bootloader |
| SRAM | 2 KB (ATmega328P-PU) |
| EEPROM | 1 KB (ATmega328P-PU) |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| LED_BUILTIN | D13 |
Features
- 1.0 pinout: added SDA and SCL pins that are near to the AREF pin and two other new pins placed near to the RESET pin, the IOREF that allow the shields to adapt to the voltage provided from the board.
- Stronger RESET circuit.
- Atmega 16U2 replace the 8U2.
PCB Dimensions
Element and Pin Interfaces
Here is an explanation chart of what every element and interface of the board does:
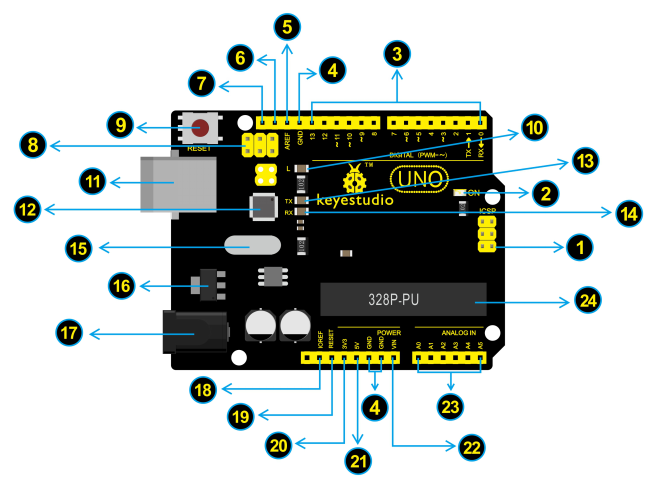
Specialized Functions of Some Pins
- Serial communication: Digital pins 0 (RX) and 1 (TX).
- PWM Interfaces (Pulse-Width Modulation): D3, D5, D6, D9, D10, D11
- External Interrupts: D2 (interrupt 0) and D3 (interrupt 1). These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value.
- SPI communication: D10 (SS), D11 (MOSI), D12 (MISO), D13 (SCK). These pins support SPI communication using the SPI library.
- IIC communication: A4 (SDA); A5(SCL)
Warnings:
1. The Arduino Uno has a resettable polyfuse that protects your computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent. If more than 500 mA is applied to the USB port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short or overload is removed.
2. Automatic (Software) Reset:
Rather than requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the Arduino Uno board is designed in a way that allows it to be reset by software running on a connected computer.
3. The Uno board contains a trace that can be cut to disable the auto-reset. The pads on either side of the trace can be soldered together to re-enable it. It's labeled "RESET-EN". You may also be able to disable the auto-reset by connecting a 110 ohm resistor from 5V to the reset line; see this forum thread for details.
Detailed Use with ARDUINO Software as follows:
Step1 | Download the Arduino environment (IDE)
When you get the UNO development board, first you should install the Arduino software and driver.
We usually use the Windows software Arduino 1.5.6 version. You can download it from the link below:
https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/OldSoftwareReleases#1.5.x
Or you can browse the ARDUINO website to download the latest version from this link, https://www.arduino.cc, pop up the following interface.

Then click the SOFTWARE on the browse bar, you will have two options ONLINE TOOLS and DOWNLOADS.

Click DOWNLOADS, it will appear the latest software version of ARDUINO 1.8.5 shown as below.

In this software page, on the right side you can see the version of development software for different operating systems. ARDUINO has a powerful compatibility. You should download the software that is compatible with the operating system of your computer.
We will take WINDOWS system as an example here. There are also two options under Windows system, one is installed version, the other is non-installed version.
For simple installed version, first click Windows Installer, you will get the following page.


This way you just need to click JUST DOWNLOAD, then click the downloaded file to install it.
For non-installed version, first click Windows ZIP file, you will also get the pop-up interface as the above figure.
Click JUST DOWNLOAD, and when the ZIP file is downloaded well to your computer, you can directly unzip the file and click the icon of ARDUINO software to start it.
Installing Arduino (Windows)
Install Arduino with the exe. Installation package
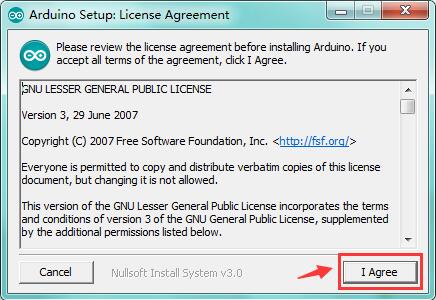
Click“I Agree”to see the following interface.
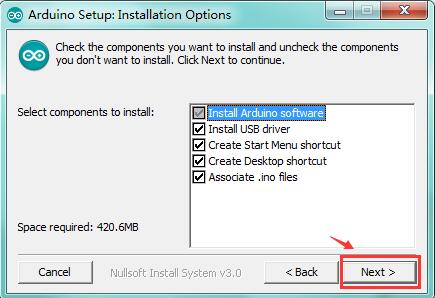
Click “Next”. Pop up the interface below.
You can press Browse… to choose an installation path or directly type in the directory you want.
Then click “Install” to initiate installation.
Wait for the installing process, if appear the interface of Window Security, just continue to click Install to finish the installation.
Installing Driver
Next, we will introduce the driver installation of UNO R3 development board. The driver installation may have slight differences in different computer systems. So in the following let’s move on to the driver installation in the WIN 7 system.
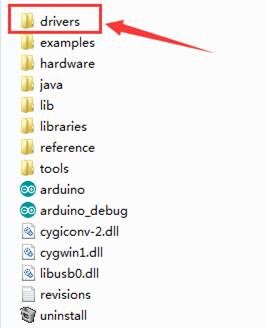
The Arduino folder contains both the Arduino program itself and the drivers that allow the Arduino to be connected to your computer by a USB cable. Before we launch the Arduino software, you are going to install the USB drivers.
Plug one end of your USB cable into the Arduino and the other into a USB socket on your computer.
When you connect UNO board to your computer at the first time, right click the icon of your “Computer” —>for “Properties”—> click the “Device manager”, under “Other Devices”, you should see an icon for “Unknown device” with a little yellow warning triangle next to it. This is your Arduino.

Then right-click on the device and select the top menu option (Update Driver Software...) shown as the figure below..

It will then be prompted to either “Search Automatically for updated driversoftware” or “Browse my computer for driver software”. Shown as below. In this page, select “Browse my computer for driver software”.
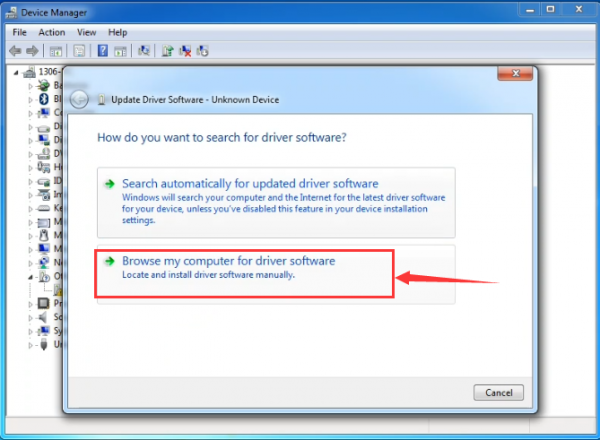
After that, select the option to browseand navigate to the “drivers” folder of Arduino installation.
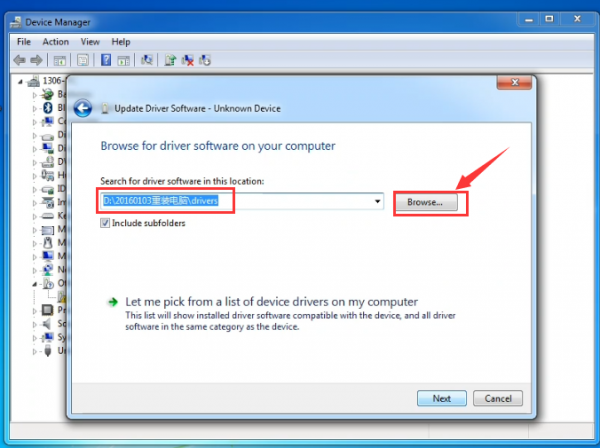
Click “Next” and you may get a security warning, if so, allow the software to be installed. Shown as below.

Once the software has been installed, you will get a confirmation message. Installation completed, click “Close”.

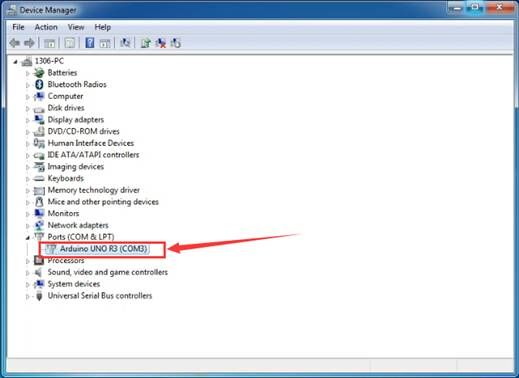
Up to now, the driver is installed well. Then you can right click “Computer” —>“Properties”—>“Device manager”, you should see the device as the figure shown below.

Introduction for Arduino IDE Toolbar
Double-click the icon of Arduino software downloaded well, you will get the interface shown below.

(Note: if the Arduino software loads in the wrong language, you can change it in the preferences dialog. See the environment page for details.)

The functions of each button on the Toolbar are listed below:
![]()
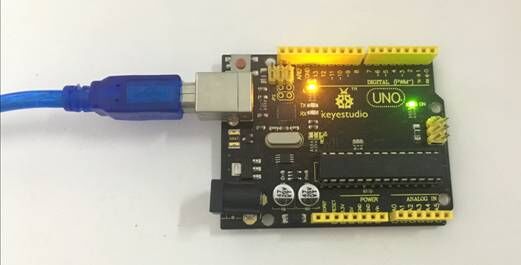
Step2| Connect the board
Connect the UNO board to your computer using the USB cable. The green power LED should go on.
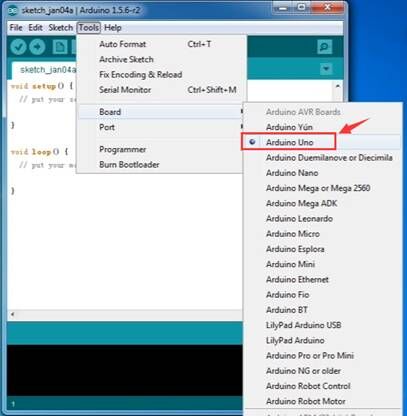
Step3| Select the Arduino Board
Open the Arduino IDE, you’ll need to click the “Tools”, then select the Board that corresponds to your Arduino.
Step4| Select the Serial Port
Select the serial device of the Arduino board from the Tools | Serial Port menu. This is likely to be COM3 or higher (COM1and COM2 are usually reserved for hardware serial ports). To find out, you can disconnect your Arduino board and re-open the menu; the entry that disappears should be the Arduino board. Reconnect the board and select that serial port.
Here you should select COM 3 as below.
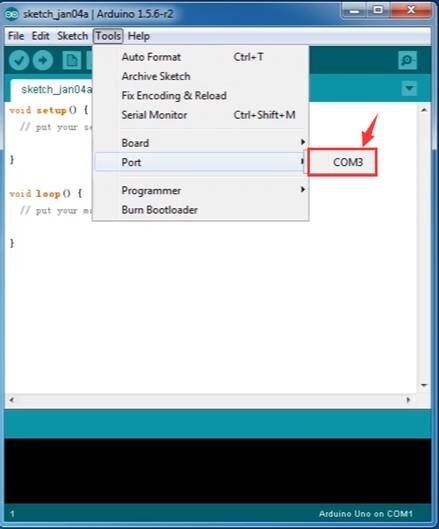
Note: to avoid errors, the COM Port should keep the same as the Ports shown on Device Manager.
Step5| Upload the Program
Below is an example program for displaying the Hello World! Copy and paste the above code to the Arduino environment IDE.
int val;
int ledpin=13;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledpin,OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
val=Serial.read();
if(val=='R')
{
digitalWrite(ledpin,HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ledpin,LOW);
delay(500);
Serial.println("Hello World!");
}
}
Then click verify button to check the errors. If compiling successfully, the message "Done compiling." will appear in the status bar.
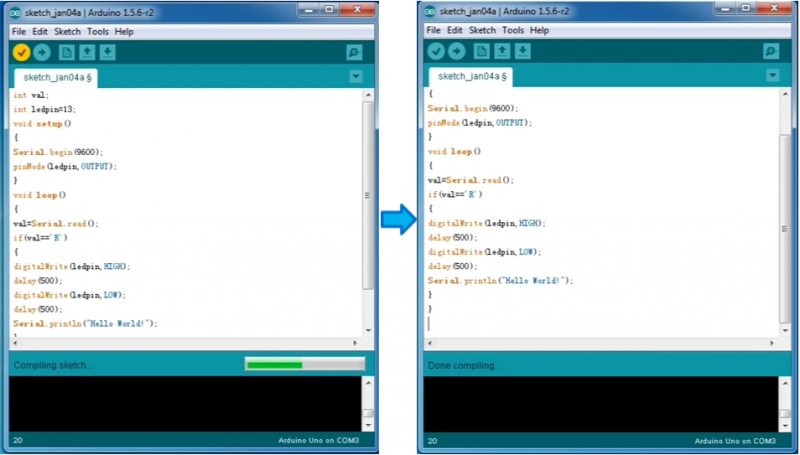
After that, click the “Upload” button to upload the code. Wait a few seconds - you should see the RX and TX leds on the board flashing. If the upload is successful, the message "Done uploading." will appear in the status bar. (Note: If you have an Arduino Mini, NG, or other board, you'll need to physically present the reset button on the board immediately before pressing the upload button.)
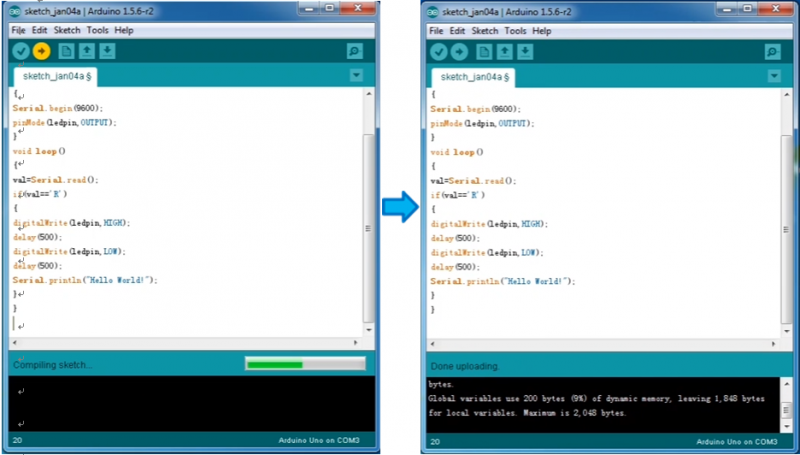
A few seconds after the upload finishes, you should see the pin 13 (L) LED on the board start to blink (in orange). If it does, congratulations! You've gotten Arduino up-and-running.
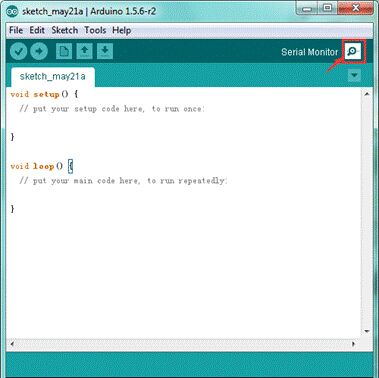
Step6| Open the Serial Monitor
After that, click the serial monitor button to open the serial monitor.
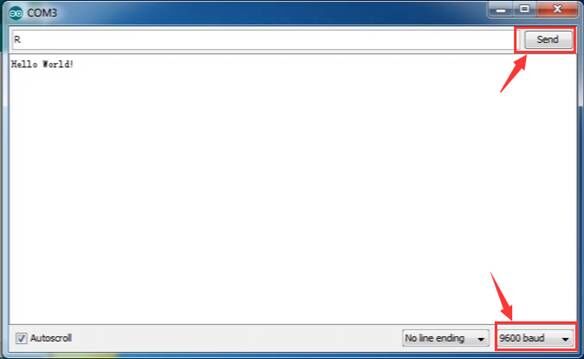
Then set the baud rate as 9600, enter an “R” and click Send, you should see the RX led on the board blink once, and then D13 led blink once, finally "Hello World!" is showed on the monitor, the TX led blink once. Congrats!
Other Links
- You might also want to look at:
the examples for using various sensors and actuators;
the reference for the Arduino language;
The text of the Arduino getting started guide is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. Code samples in the guide are released into the public domain.
- You can download the datasheet from the link:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1PQnMRVBaPwLdfzw_7T3OlLhOyEP0rY_S
- Software Download:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=12D-JkXdNm03Qt4dlPQr3RP6OmgXqpvHc
Troubleshooting
If you have problems, please see the troubleshooting suggestions.
Extensions
Resources
Video:
http://www.keyestudio.com/wp/ks0001/
Datasheet:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1y8RXlk26EeU0FfdZ825LTaBoqxtsez-i
Get One Now
- Official Website
http://www.keyestudio.com/ks0001.html